Contents
- 1 CYCLING: ENHANCING YOUR RIDE
- 1.1 I. Understanding the Essentials
- 1.2 II. Performance-Enhancing Accessories Cycling Gear
- 1.3 III. Maintenance and Comfort Tools
- 1.4 IV. Transport and Storage Solutions
- 1.5 Conclusion
CYCLING: ENHANCING YOUR RIDE

Having the right cycling gear and accessories for cycling is crucial for several reasons, enhancing safety, comfort, and overall riding experience. Quality helmets and protective gear safeguard against injuries, while appropriate clothing can shield riders from various weather conditions, maintaining comfort and focus.
For comfort, ergonomic design in seating, clothing tailored for riding posture, and gloves reduce strain and prevent injuries, allowing for longer, more enjoyable rides. Performance gains are seen through efficient, well-fitted gear like aerodynamic helmets and moisture-wicking apparel, which can improve speed and endurance by reducing air resistance and managing sweat.
Tailored cycling shoes and gloves improve grip and control, directly influencing performance and endurance. Furthermore, essential accessories like lights, reflectors, and maintenance tools ensure that cyclists are prepared for any situation, be it navigating in low visibility or performing roadside repairs.
In terms of safety, high-quality helmets and protective pads offer critical impact protection, while lights and reflective materials ensure visibility to others, crucial for preventing accidents. Thus, selecting the appropriate cycling gear and accessories is vital for a safer, more effective, and comfortable cycling experience.
I. Understanding the Essentials
Helmets: Safety and Comfort
Injury Prevention: The primary purpose of a helmet is to
protect the rider’s head in the event of a crash. It acts as a barrier between the head and the impact surface, absorbing and distributing the force of the impact, which can significantly reduce the severity of head injuries. In many places, wearing a helmet while cycling is mandated by law, especially for children. Failing to wear a helmet can lead to fines and also indicates non-compliance with road safety regulations.
crash. It acts as a barrier between the head and the impact surface, absorbing and distributing the force of the impact, which can significantly reduce the severity of head injuries. In many places, wearing a helmet while cycling is mandated by law, especially for children. Failing to wear a helmet can lead to fines and also indicates non-compliance with road safety regulations.
Risk Reduction:
Research has shown that cyclists who wear helmets reduce their risk of head injuries by a significant margin. Helmets are particularly effective in protecting against skull fractures and serious brain injuries. Modern helmets are equipped with additional features like visors, which protect eyes from the sun and debris, and ventilation holes to keep the head cool, improving the overall cycling experience.
Overall, wearing a helmet is a simple yet effective measure that plays a crucial role in safeguarding cyclists from serious injuries, promoting a culture of safety, and enhancing the cycling experience.
Key Features To Look For
Good airflow is crucial, especially on long rides or in hot weather.
Look for helmets with multiple and strategically placed vents that allow for efficient air circulation, helping to keep your head cool and reduce sweat buildup.
and strategically placed vents that allow for efficient air circulation, helping to keep your head cool and reduce sweat buildup.
A proper fit is essential for a helmet to provide maximum protection. The helmet should sit snugly on your head without being too tight, with an adjustable retention system at the back to secure it in place. It should sit level on your head and not rock forward, backward, or side to side. The straps should form a “V” around each ear and fasten securely under the chin.
A lighter helmet can reduce neck fatigue and make the riding experience more comfortable, especially over long distances. Advanced materials and design technologies allow for lightweight helmets that still provide strong impact protection.
Helmets with adjustable straps and retention systems offer a more personalized fit, enhancing comfort and safety. Look for helmets with easy-to-use adjustment mechanisms that can be handled even while riding.
Safety Features
Advanced safety features like MIPS
(Multi-directional Impact Protection System) offer additional protection against rotational forces in the event of an angled impact. Some helmets also come with integrated LED lights for increased visibility and safety.
protection against rotational forces in the event of an angled impact. Some helmets also come with integrated LED lights for increased visibility and safety.
While not impacting safety directly, the design and aesthetics of a helmet can be important for personal preference and confidence while riding. Helmets come in various styles and colors to match different tastes and cycling gear.
By considering these features, cyclists can choose a helmet that not only meets safety standards but also fits well, is comfortable to wear, and suits their riding style and preferences.
Clothing: Dress for the Ride
Cycling clothing is often form-fitting, reducing air resistance and improving efficiency. This can be especially beneficial for road cycling, where even minor reductions in drag can significantly affect performance over time.
Made from technical fabrics, cycling wear is designed to wick sweat away
from the skin, keeping the rider dry and comfortable. This helps to regulate body temperature and prevent overheating or chilling during rides. Features like flat seams, padding, and stretchable fabrics reduce chafing, discomfort, and muscle fatigue. Specifically, padded shorts or bibs can significantly increase comfort on long rides by cushioning the sit bones and reducing pressure points.
Cycling clothing can be optimized for different weather conditions. For example, thermal fabrics are used for cold-weather gear to retain body heat, while lightweight and breathable materials are used in summer clothing to help cool down the body
Many cycling garments offer protection against the elements, including windproof and waterproof materials for inclement weather. UV-protective fabrics also shield the skin from harmful sun exposure during long rides.
Cycling-specific clothing often includes design elements like back pockets on jerseys for easy access to snacks, tools, and other essentials. Reflective elements and bright colors can also improve visibility and safety on the road. Cycling clothes are designed to accommodate the cyclist’s posture and movements, with cuts that allow for a full range of motion in the cycling position, preventing the fabric from bunching up or restricting movement.
Designed to withstand the rigors of cycling, such clothing is made from strong, abrasion-resistant materials that can endure repeated use and washing, as well as contact with Velcro and other fasteners.
Layering for weather conditions with your cycling gear
The foundation of layering, the base layer, is worn directly against the skin. Its primary function is moisture management, wicking sweat away to keep the skin dry and regulate body temperature. For hot conditions, a thin, breathable base layer helps with cooling, while in colder weather, a thicker, insulating base layer is ideal for retaining body heat.
The mid layer provides insulation and continues the process of transferring moisture from the base layer to the outer layer. In cool conditions, a mid layer like a long-sleeve jersey or a fleece jacket can be added for warmth. For colder weather, heavier materials like thermal fabrics are preferred to maintain body heat.
The outer layer is the protective shell against wind, rain,
and external cold. A good outer layer is windproof and waterproof yet breathable, preventing windchill and moisture from penetrating while allowing sweat vapor to escape. Options include, lightweight windbreakers for mild conditions and heavier, waterproof jackets for harsh weather.
Depending on the weather, various accessories can complement the three main layers. For cold conditions Gloves, thermal socks, shoe covers, caps, and neck warmers provide additional insulation. For warmer weather, Lightweight gloves, arm and leg sleeves, and caps protect against sunburn while allowing for adjustable coverage.
Layering should be adaptable to changing conditions. Cyclists should be able to add or remove layers easily. Garments with full zippers, vents, and detachable sleeves offer flexibility to respond to temperature variations and physical exertion levels.
Choose materials that are suitable for the specific conditions. For example, merino wool is excellent for a range of temperatures, providing warmth even when wet, while synthetic fabrics are known for their quick-drying and sweat-wicking properties. Additionally, ensure that all layers fit well together without restricting movement. Layers should be snug but not too tight, allowing for a range of motion and preventing fabric from bunching up, which can lead to discomfort or chafing.
Footwear: Connecting with Your Bike
Benefits of cycling shoes. Efficient Power Transfer:
Cycling shoes have stiff soles that provide a solid platform for pedaling.
This stiffness ensures that less energy is lost in the flex of the shoe, translating more power directly to the pedals, which increases riding efficiency.
less energy is lost in the flex of the shoe, translating more power directly to the pedals, which increases riding efficiency.
Secure Fit: These shoes are designed to fit snugly and securely, reducing the risk of slipping or foot movement inside the shoe while pedaling. This secure fit helps in maintaining consistent pedaling mechanics and reduces the risk of blisters or foot discomfort.
Cleat Compatibility: Cycling shoes can be equipped with cleats that clip into the pedals of the bike. This connection, known as clipless pedal systems, allows for a more secure attachment to the bike, which improves control and allows the cyclist to pull up on the pedals as well as push down, enabling a more effective and full circular pedal stroke.
They are designed to support the foot in a stable position, reducing the strain on the foot muscles and joints over long periods of cycling. The even distribution of pressure helps to prevent numbness and hot spots.
Many cycling shoes are made with materials that enhance breathability, keeping feet cooler and reducing sweat buildup. This is particularly beneficial in warm weather or during intense rides.
Designed to withstand the rigors of cycling, these shoes are made with durable materials that can handle the stress of regular riding, including the pressure exerted during pedaling and the wear and tear from the outdoor environment.
Increased Safety: The improved control and stability offered by cycling shoes can contribute to overall safety on the bike, especially when riding at high speeds or navigating tricky terrain.
II. Performance-Enhancing Accessories Cycling Gear
Bike Computers and GPS Devices
Data tracking devices can track vital cycling metrics such as speed,
distance, cadence, heart rate,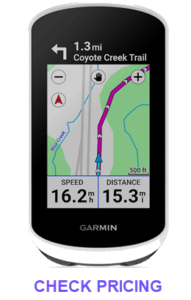 and power output. This data allows cyclists to monitor their performance over time, set specific training goals, and make informed adjustments to their training plans. Many bike computers offer features for creating and following structured workouts, which can be tailored to improve specific aspects of a cyclist’s performance, such as endurance, speed, or climbing ability.
and power output. This data allows cyclists to monitor their performance over time, set specific training goals, and make informed adjustments to their training plans. Many bike computers offer features for creating and following structured workouts, which can be tailored to improve specific aspects of a cyclist’s performance, such as endurance, speed, or climbing ability.
By consistently tracking performance data, cyclists can see their progress over time. This not only helps in fine-tuning training but also in maintaining motivation and setting new goals.
GPS-enabled devices provide real-time mapping and navigation, helping cyclists to explore new routes safely and confidently. They can display preloaded routes or allow riders to create their own, ensuring they stay on course. Like car navigation systems, many bike GPS units offer turn-by-turn directions, making it easier to follow complex routes without constantly stopping to check maps.
Off-Road Navigation: For mountain bikers and adventure cyclists, these devices can be invaluable in navigating off-road trails and unfamiliar terrain, reducing the risk of getting lost. Some devices offer live tracking features that allow friends or family to monitor the cyclist’s location in real-time, enhancing safety during solo rides, especially in remote areas.
Advanced units may include incident detection sensors that can automatically alert emergency contacts in the event of a crash, providing an additional layer of safety. Many bike computers and GPS devices can connect to various cycling apps and online services, allowing riders to upload their ride data, analyze it in more detail, and share it with others in the cycling community.
Smart Notifications
Connected devices can display notifications for calls, texts, and app alerts directly on the screen, so cyclists can stay connected without needing to pull out their smartphone.
In conclusion, bike computers and GPS devices enrich the cycling experience by providing detailed data for training optimization, offering advanced navigation tools, enhancing rider safety, and allowing for greater connectivity. These features make them essential tools for both recreational and serious cyclists.
Key features and popular models
Garmin Edge Series (e.g., Edge 530, Edge 830, Edge 1030 Plus)
Known for robust GPS features, comprehensive data tracking, and extensive connectivity options. Models range from basic to advanced, catering to casual cyclists and competitive athletes alike.
Wahoo ELEMNT Series (e.g., ELEMNT ROAM, ELEMNT BOLT)
Praised for their user-friendly interface, clear navigation, and seamless smartphone integration. Offer excellent battery life and customizable data screens.
Hammerhead Karoo 2
Features a large, color touchscreen with a user-friendly interface.
Offers detailed mapping and navigation, along with powerful data processing capabilities.
Bryton Rider Series (e.g., Rider 750, Rider 420)
Known for good value, offering essential GPS and data tracking features at more accessible price points. Offer solid battery life and compatibility with various sensors.
Lezyne GPS Units (e.g., Mega XL, Super Pro GPS)
Compact and durable with a focus on core functionality and straightforward navigation. Good battery life and an attractive price-to-feature ratio.
Lights and Reflective Gear
Lights and reflective gear make cyclists more visible to drivers,
pedestrians, and other cyclists. This is crucial for preventing accidents, especially at intersections, in urban areas, or on roads without dedicated cycling paths. Front lights help cyclists see the road ahead, illuminating potential hazards like potholes, debris, and sharp bends. Good lighting is essential for safe navigation in dark conditions.
This is crucial for preventing accidents, especially at intersections, in urban areas, or on roads without dedicated cycling paths. Front lights help cyclists see the road ahead, illuminating potential hazards like potholes, debris, and sharp bends. Good lighting is essential for safe navigation in dark conditions.
In many regions, the law requires bicycles to have front and rear lights activated during night riding or in poor visibility conditions. Reflective gear, while not always mandatory, is strongly recommended to enhance visibility. In addition to constant lighting, blinking lights can be used to signal a cyclist’s presence and draw attention to their movements, helping to communicate intentions and movements to others on the road.
Modern cycling lights are designed to be lightweight, durable, and easy to attach to bikes, helmets, or clothing. Reflective gear, including vests, jackets, and strips, can be worn over regular clothing, making it a flexible safety feature.
Reflective materials on clothing, helmets, and accessories like gloves or shoes catch and bounce back light sources, such as car headlights, significantly increasing a cyclist’s visibility. This is particularly effective during twilight hours or in urban areas with varying light conditions. Visible cyclists can deter potential accidents by alerting drivers and others of their presence well in advance, allowing for more reaction time to avoid close encounters or collisions.
Hydration and Nutrition Solutions
Options for carrying water and food. Water Bottles and Cages:
The most common method is using water bottles stored in cages attached to the bike frame. Some bikes can accommodate multiple cages, allowing cyclists to carry more water for longer rides.
water bottles stored in cages attached to the bike frame. Some bikes can accommodate multiple cages, allowing cyclists to carry more water for longer rides.
Hydration Packs: A hydration pack is a backpack or waist pack with a built-in water reservoir, or bladder, and a hose that allows the rider to drink without stopping. These are especially popular among mountain bikers and for longer endurance rides.
For triathletes and time trialists, aero drink systems can be mounted on the handlebars or between aero bars, providing easy access to fluids without disrupting aerodynamics.
Insulated water bottles can keep liquids cool for several hours, which is ideal for cycling in hot weather conditions.
Nutrition Solutions
Cycling jerseys typically have rear pockets where riders can store energy bars, gels, and other small snacks for easy access while riding.
Top tube bags, also known as bento boxes attach to the top tube
and stem of the bike, offering convenient access to snacks without needing to stop or reach into a jersey pocket. larger saddle bags can also accommodate extra nutrition items. For longer rides, handlebar bags can carry more substantial food items, along with other essentials like extra clothing or electronics.
convenient access to snacks without needing to stop or reach into a jersey pocket. larger saddle bags can also accommodate extra nutrition items. For longer rides, handlebar bags can carry more substantial food items, along with other essentials like extra clothing or electronics.
Frame bags are ideal for bike packing or long-distance touring, frame bags fit within the bike’s frame triangle and can hold larger quantities of food and water, along with other gear.
III. Maintenance and Comfort Tools
Cycling Gear Repair Kits and Multi-Tools
A cycling-specific multi-tool typically includes various sizes of hex keys
(Allen wrenches), screwdrivers (flathead and Phillips), and sometimes a Torx driver, which are necessary for adjusting or repairing various parts of the bike, such as the saddle height, handlebars, or brakes.
screwdrivers (flathead and Phillips), and sometimes a Torx driver, which are necessary for adjusting or repairing various parts of the bike, such as the saddle height, handlebars, or brakes.
Tire levers are used to remove the tire from the rim when fixing a flat tire or replacing the tube. They come in compact sizes that are easy to carry. Carrying at least one spare inner tube is crucial for quickly fixing a flat tire. Alternatively, or in addition, a patch kit can be used to repair punctured tubes.
A small hand pump or CO2 inflator is necessary to re-inflate tires after repairing a flat. CO2 inflators are faster and more compact but require cartridges, while hand pumps are more reliable and reusable.
A broken chain can end a ride prematurely. A chain tool is used to remove damaged links, and spare links or a quick link can be used to reconnect the chain. If the bike has parts that require a wrench, carrying a small adjustable wrench can be helpful.
Carry a cloth or gloves To keep hands clean during repairs and to wipe off any dirt or grease from bike parts after fixing an issue.
Optional Items
Brake and Derailleur Cables: Having spare cables can be a lifesaver if one breaks during a ride. Zip ties and Duct tape can provide temporary fixes for a variety of issues, from securing loose components to patching up damaged gear. A tire boot (or even a sturdy piece of material) can temporarily patch a significant tire cut, allowing you to ride to a more permanent repair location.
Most cyclists carry their repair kit in a small saddle bag attached under the seat, but other options include frame bags, backpacks, or even jersey pockets for smaller items. It’s important to familiarize yourself with how to use each tool and perform common repairs before heading out on a ride, as having the tools is only beneficial if you know how to use them effectively.
IV. Transport and Storage Solutions
Bike Racks and Carriers
Bikes are mounted on the roof of the car, freeing up space inside the vehicle. This option is good for taller vehicles and when you need to transport several bikes.
Hitch Racks attached to the vehicle’s hitch receiver, these racks are easy to load and can carry multiple bikes without the need to lift them high off the ground.
Trunk Racks are attached to the rear of the car using straps and can be a more affordable and versatile option.
versatile option.
For air travel or long-distance transport, hardshell bike cases and padded bags protect the bike from damage. These require partial disassembly of the bike (like removing wheels and pedals) for a secure fit.
Bikes can often be taken on public transport systems, such as trains or buses, though it’s important to check the specific rules and times when bikes are allowed.
Storage Solutions
Bikes can be hung by the frame or wheel, saving floor space in your home or garage. Various designs exist, from hooks and brackets to sophisticated systems that allow for horizontal or vertical storage. Floor Stands allow bikes to be parked upright without needing to lean against a wall or other object. Some stands hold the bike at the wheel, while others support it by the frame.
Ceiling Hoists can be used for high-ceiling spaces. hoists can lift and suspend the bike off the ground, freeing up floor and wall space. Secure bike sheds or outdoor storage units can protect bikes from the weather and theft, ideal for those with limited indoor space.
Conclusion
Choosing the right cycling gear and accessories is paramount to ensuring a safe, comfortable, and enjoyable cycling experience. The appropriate gear can significantly enhance performance, aid in navigation, increase safety, and make the overall cycling journey more pleasurable. From helmets that protect against head injuries to lights and reflective gear that enhance visibility, each piece of equipment plays a crucial role in preparing cyclists for various scenarios they may encounter on the road or trail.
Investing in quality cycling accessories, such as reliable bike computers and GPS devices, can transform rides into more efficient training sessions and enjoyable explorations, allowing cyclists to track performance data, navigate routes confidently, and stay connected. Furthermore, ergonomic clothing and shoes can prevent discomfort and injuries, while specialized repair kits and multi-tools ensure that cyclists are prepared for mechanical issues, minimizing downtime and frustration during rides.
We earn from qualified Amazon purchases with NO cost to you. ANY item that you need or were going to purchased anyway through any of our links, helps support this site. Thank you for your support!


